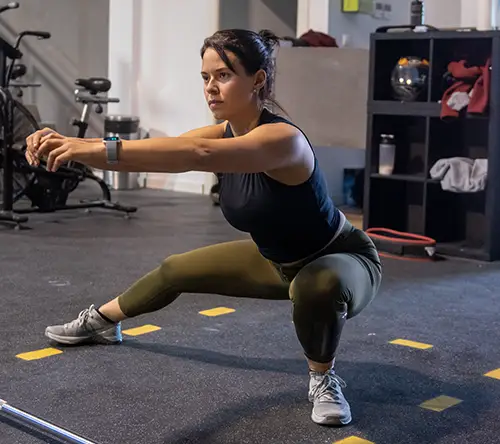
Squat
This exercise is one of the CrossFit Fundamentals on which other movements of greater difficulty are built.
In this post we will analyze the technique for a good squat, common mistakes and how to fix them.
What does a squat look like?
The starting position is upright with feet hip-width apart. From here the athlete bend your knees and descend with your hips backwards and downwards, looking to break the imaginary line of 90º. the hip forms with the knees. Again the starting position is regained with a full hip extension.
This range of motion is common to all versions of the squat, although each has its peculiarities.
Benefits of squats
Squat work is very important in a sport like CrossFit.
The muscles of the legs quadriceps, hamstrings, adductors and calf muscles are involved in many exercises such as weightlifting, where leg strength and power are essential.
Types of squat
Air squat
It is performed without weight.
It is the version most basic of all, but the most important.
If your air squat is not good, this will have repercussions on the movement pattern of the other squat versions and you will not be able to exploit your potential, as you will quickly reach your limit.
Working muscles: quadriceps, and to a lesser extent hamstring and gluteus maximus.
Common errors
- Do not break the parallel: the range of motion must be complete.
SolutionIn case of proprioception or flexibility problems, the use of a box to check the depth of the squat is recommended.
- Lifting the heels: this is a sign of lack of mobility in the heels and hips.
Solution: work with a lot of patience, mobility. Consult this post to help you with that work.
Back squat
The movement pattern is the same as in the non-weighted squat, but this time it is load the bar behind the neck resting on the trapezius muscles.
Working muscles: quadriceps, and to a lesser extent the back erectors, hamstrings and gluteus maximus.
Common errors
- Bringing the knees to the center when we lift the weight: this is an indicator that the weight is greater than the force our gluteus can do to keep the knees aligned.
Solutiongluteal accessory work
Front squat
Unlike the back squat, the weight is front loaded, supported at the shoulders while the elbows are kept elevated.
Working muscles: quadriceps, and to a lesser extent the core, hamstring and gluteus maximus.
gravity is the main factor in the front load. forces the abdominal area to become much more active.
Weight is usually a 70-85% in relation to the back squat.
Common errors
- Forward overcoming: when the load starts to be a challenge, it is common to see the elbows drop, the chest sinks and the athlete forwards overcomes, often even losing the bar.
Solution: concentrate on keeping your elbows elevated and lower the load if you are unable to maintain your posture.
Overhead squat
In this case, the bar is above the head, normally with a wide grip although no specific hand position is required.
This is the version that requires the most skills, since in addition to the strength, balance and flexibility are needed to maintain the load.
Working muscles: quadriceps and trapezius. To a lesser extent triceps, core, hamstrings and gluteus maximus.
The percentage of weight is usually a 50-60% Back Squat 50-60%.
Common errors
- The bar falls in front of the frontal plane: usually indicates limited mobility.
Solution: can help open the hand grip while working on mobility.
If you need to improve this movement, Ales Faus, physio specialized in CrossFit, brings us the most important aspects to master this movement along with the exercises you should perform according to your weaknesses.
Pistol squat or one-legged squat
This is the version with the most differences over all the previous ones. In this case the squat is performed on one foot only.
Working musclesGlutes, hamstrings and quadriceps.
This is an advanced exercise. In order to achieve the technique, the following progressions are proposed:
- Isometric strength at height. Use a higher platform, such as a box box, to do negative pistol work, i.e. controlling your weight while lowering your body supported on one leg.
- Isometric strength on the ground. The next level is to do it on the floor. Controlling the descent with one leg and supporting the other leg to go up in a normal squat.
- Pistol with assistance. It is the last step before making the pistol. You can help yourself with a rubber band, lean on a rack... to assist the ascent. It is important that you have worked the other steps before so that the assistance is minimal and you are close to doing the pistol in RX (without assistance).
Common errors
- The heel is lifted, here even more pronounced than in the other versions of the squat.
Solution: working on mobility.
Trick: You can also help yourself with the weightlifting shoes that by having the heel elevated give you the plus you need. But keep in mind that if you don't work on your mobility you will always depend on them.
- The extended foot touches the ground. This is a problem, because even if you don't want to use it as a support, if the heel comes into contact with the ground you get a no rep.
Solution: work on the flexibility of the hamstrings to keep the leg straight in a more comfortable way.
Trick: In the meantime, you can grab the tip of your toe with your hands to prevent it from touching the ground.
Don't miss this complete article with progressions for the pistol squat:
Cossack squat or side squat
This one-legged squat is a variation that helps develop mobility, flexibility and strength in the frontal plane.
Consists of making the squat with one supporting leg in the normal position, and another in the form of a lateral split.The weight of the load is very low.
You start with your legs wider apart than in a normal squat, so that you can shift your body to one side. Perform the squat and return to the center.
Working musclesadductors, hamstrings, quadriceps and gluteus muscles
This is not an exercise that we usually see in the WOD but in the previous more technical part of strength/skill, or even in the warm-up.
The exercise can be performed with your own body weight or by adding a load: dumbbell, kettlebell, bar or even vest.
Goblet Squat
Maybe because of that name the movement doesn't come to your mind (even less if I tell you the name in Spanish: sentadilla con copa), but we do this exercise a lot in the box.
The goblet squat is a strength exercise that consists of performing a front squat while holding a dumbbell or kettlebell in the center of the chest. Although a disc or any weighty object can also be used.
The athlete holds the weight with hands together in the center of the chest, elbows close to the body, and then bends at the knees to lower down to break parallel with the hips. Then push with the legs to return to the starting position and complete one repetition. This exercise works the leg muscles, especially the quadriceps and glutes.
The clear advantage provided by this squat variant is that it you don't need a bar and discs for training.
On the other hand, if the goal of training with heavy loads, it will not be feasible.
Working muscles: mainly quadriceps. Also hamstrings, glutes, core and shoulders.
Accessories for squats
The most common are:
- Weightlifting shoesThe heel is not only more stable as it is a hard-soled shoe, but the heel has more height, which helps to compensate for ankle mobility problems.
- Lumbar beltin very heavy lifting, it can provide extra reinforcement in the lumbar area.
- Knee padsalso designed to give added reinforcement in high lifts.
- Wristbands: for the overhead squat especially. The load can be uncomfortable for the wrists with the hands carrying in a wide grip. Wrist straps thanks to compression help improve the feel.